Abstract

Background
Current NCCN and ELN guidelines lack supporting evidence in regards to initiation of cytoreductive therapy in essential thrombocythemia (ET) with extreme thrombocytosis (ExT) ≥1500 x 10 9/L (NCCN guidelines: myeloproliferative neoplasms, version 2. 2019, Barbui, Leukemia, 2018).; we sought to determine prevalence and establish phenotype and genotype correlates for ET with ExT and assess its impact on thrombotic and bleeding events, in the context of aspirin therapy or cytoreduction.
Methods
1,249 WHO-defined ET patients evaluated over five decades (1967-2021) were retrospectively recruited from the Mayo Clinic. Conventional criteria were used to define major arterial and venous thrombosis and major hemorrhage. Conventional statistical methods were applied using JMP Pro 14.0.0 software package, SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
Results
i) Phenotype and genotype correlates
Among 1,249 consecutive patients with ET, 104 (8%) displayed Ext ≥1500 x 10 9/L, at time of initial diagnosis; these patients were characterized by younger age (median 47 vs 59 years; p<0.001) female gender (80% vs 62%; p<0.001), CALR mutation (39% vs 25%; p=0.004), lower hemoglobin (median 13.1 vs 13.7 g/dl; p<0.0001), leukocytosis ≥11 x 10 9/l (42% vs 23%; p<0.0001), and palpable splenomegaly (22% vs 14%; 0.03); multivariable analysis confirmed associations with age, anemia, leukocytosis, and CALR mutation. Acquired von Willebrand syndrome was reported in 4/9 (44%) vs 27/78 (35%) tested patients, with or without Ext ≥1500 x 10 9/L, respectively (p=0.57); however, comparison using platelet ≥1000 x 10 9/L resulted in near-signficant difference (46% vs 29%; p=0.11). NGS was performed in 297 patients and showed a non-sigificant association with U2AF1 mutations (5% vs 0.4%; p=0.11). ExT ≥1500 x 10 9/L was present in 25/986 (3%), 42/891 (5%), and 15/558 (3%) in the validation cohort; the limited number of cases precluded comparative analyses.
ii )Correlation with vascular events at/prior to diagnosis
Arterial or venous thrombosis at/prior to diagnosis occurred in 190 (15%) and 111 (9%) patients, respectively, and major hemorrage in 50 (4%). Ext ≥1500 x 10 9/L was associated with major hemorrhage (HR 2.9; 1.3-6.3), but not with arterial (p=0.15) or venous (p=0.41) thrombotic events, at/prior to diagnosis. Instead, multivariable analysis for events at/prior to diagnosis identified male gender (p=0.02), JAK2 mutation (p=0.01), and cardiovascular risk factors (p=0.001) as risk factors for arterial thrombosis and JAK2 mutation (HR 2.8; 1.4-5.7) as a risk factor for venous thrombosis.
iii )Correlation with vascular events after diagnosis
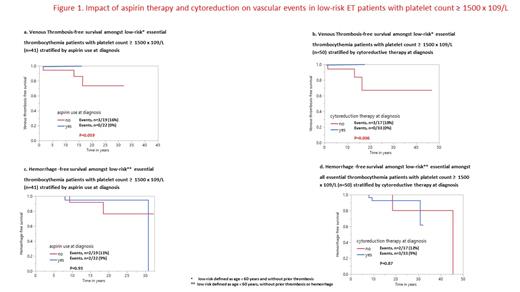
At median follow-up of 10 years, arterial or venous thrombosis occurred in 222 (18%) and 97 (8%) patients, respectively, and major hemorrage in 128 (11%). Ext ≥1500 x 10 9/L at diagnosis was not associated with arterial (p=0.35) or venous (p=0.23) thrombosis-free survival or hemorrhage-free survival (p=0.24). Instead, multivariable analysis identified age >60 years, presence of cardiovascular risk factors, and history of arterial thrombosis, as risk factors for arterial thrombosis-free survival; and male gender and history of venous thrombosis as risk factors for venous thrombosis-free survival; and age >60 years and leukocytosis of ≥11 x 10 9/L as risk factors for hemorrhage-free survival. In addition, aspirin therapy was idependently protective of venous thrombosis (HR 0.5; 0.2-0.9), and also of arterial thrombosis, in univariate analysis (HR 0.6; 0.3-0.9), without being associated with an increased risk of major hemorrhage (p=0.64); by contrast, beneficial effect from cytoreductive therapy was not evident for either arterial (p=0.37) or venous (p=0.77) thrombosis. In low-risk patients with Ext ≥1500 x 10 9/L, both aspirin and cytoreductive therapy were protective of venous events (Figure 1), without affecting hemorrhage-free survival.
Conclusion
ExT ≥1500 x 10 9/L in ET was associated with major hemorrhage at diagnosis but did not affect thrombosis-free or hemorrhage-free survival. Initial therapy with aspirin and/or cytoreductive therapy was protective of venous events in ET patients with ExT ≥1500 x 10 9/L, including those with low-risk disease, without enhancing the risk of hemorrhage. The limited number of informative cases with ExT in the validation cohort, underscore the foreseeable challenges associated with controlled studies.
Szuber: Novartis: Honoraria. Vannucchi: AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte Corporation: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Barbui: AOP Orphan: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal